Multirate
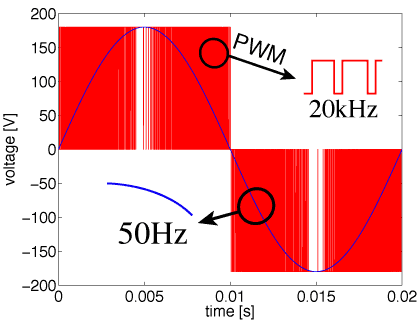
Highly integrated electric cicuits show a phenomenon called latency. That is, a processed signal causes activity only in a small subset of the whole circuit (imagine a central processing unit), whereas the other part of the system behaves almost constant over some time - is latent. Such an electric system can be described as coupled system, where the waveforms show different time scales, also refered to as multirate.
More generally, any coupled problem formulation due to coupled physical effects, may cause a multirate problem: image the simulation of car driving on the road, there you need a model for the wheel, the chassis, the dampers, the road,... (cf. co-simulation). Again each system is covered by their own time constant, which might vary over several orders of magnitude comparing different subsystems.
Classical methods cannot exploit this multirate potential, but resolve everything on the finest scale. This causes an over sampling of the latent components. In constrast, Co-simulation or especially dedicated multirate methods are designed to use the inherent step size to resolve the time-domain behaviour of each subystem with the required accuracy. This requires a time-stepping for each.
Group members working in that field
- Andreas Bartel
- Michael Günther
Former and ongoing Projects
Cooperations
- Herbert de Gersem, K.U. Leuven, Belgium
- Jan ter Maten, TU Eindhoven and NXP, the Netherlands
Publications
- 2019
4117.
Hartikainen, Markus; Miettinen, Kaisa; Klamroth, Kathrin
Interactive nonconvex Pareto navigator for multiobjective optimization
European Journal of Operational Research, 275 (1) :238-251
20194116.
Pulch, Roland; Putek, Piotr; De Gersem, Herbert; Gillon, Renaud
Inverse modeling: Glue-Package-Die problem
In ter Maten, E. Jan W. and Brachtendorf, Hans-Georg and Pulch, Roland and Schoenmaker, Wim and De Gersem, Herbert, Editor aus Mathematics in Industry
Seite 279–289
Herausgeber: Springer Cham
2019
279–2894115.
Ehrhardt, Matthias; Vázquez, Carlos
Jump-diffusion models with two stochastic factors for pricing swing options in electricity markets with partial-integro differential equations
Applied Numerical Mathematics, 139 :77–92
2019
Herausgeber: North-Holland4114.
Ehrhardt, Matthias; Vázquez, Carlos
Jump-diffusion models with two stochastic factors for pricing swing options in electricity markets with partial-integro differential equations
Applied Numerical Mathematics, 139 :77--92
2019
Herausgeber: North-Holland4113.
Ehrhardt, Matthias; Vázquez, Carlos
Jump-diffusion models with two stochastic factors for pricing swing options in electricity markets with partial-integro differential equations
Applied Numerical Mathematics, 139 :77–92
2019
Herausgeber: North-Holland4112.
Kleefeldt, Simon; Bohrmann-Linde, Claudia
Keep Track of The Heat
20194111.
Griebel, M.; Rieger, C.; Zaspel, Peter
Kernel-based stochastic collocation for the random two-phase Navier-Stokes equations
IJUQ, 9 (5)
20194110.
Jensen, Per
Linear and bent triatomic molecules are not qualitatively different!
Canadian Journal of Physics :1-6
2019
Herausgeber: NRC Research Press4109.
Bolten, Matthias; Claus, L.
Local Fourier Analysis of multigrid methods for the Stokes problem
PAMM, 19 :e201900394
20194108.
Bolten, M.; Claus, L.
Local Fourier Analysis of multigrid methods for the Stokes problem
PAMM, 19 :e201900394
20194107.
Bolten, M.; Claus, L.
Local Fourier Analysis of multigrid methods for the Stokes problem
PAMM, 19 :e201900394
20194106.
Glück, Jochen; Wolff, Manfred P. H.
Long-term analysis of positive operator semigroups via asymptotic domination
Positivity, 23 (5) :1113--1146
20194105.
Ehrhardt, Matthias; Gašper, Ján; Kilianová, Sona
Mathematical Modeling of an SIR-based infectious disease model with vaccination and waning immunity
20194104.
Gerlach, Moritz; Glück, Jochen
Mean ergodicity vs weak almost periodicity
Studia Math., 248 (1) :45--56
20194103.
[german] Yurdanur, Yasemin; Tausch, Michael W.
Metamorphoses of an Experiment - From Hightech UV Immersion Lamp Reactor to Low-Cost TicTac\(^{®}\)-Cell
{CHEMKON}, 26 (3) :125--129
2019
Herausgeber: Wiley4102.
Schulze, Britta; Stiglmayr, Michael; Klamroth, Kathrin
Multi-Objective Unconstrained Combinatorial Optimization: A Polynomial Bound on the Number of Extreme Supported Solutions
Journal of Global Optimization, 74 (3) :495–522
20194101.
Friedhoff, S.; Hahne, J.; Schöps, S.
Multigrid-reduction-in-time for Eddy Current problems
PAMM, 19 (1) :e201900262
20194100.
Friedhoff, S.; Hahne, J.; Schöps, S.
Multigrid-reduction-in-time for Eddy Current problems
PAMM, 19 (1) :e201900262
20194099.
Friedhoff, S.; Hahne, J.; Schöps, S.
Multigrid-reduction-in-time for Eddy Current problems
PAMM, 19 (1) :e201900262
20194098.
Hachtel, Christoph; Bartel, Andreas; Günther, Michael; Sandu, Adrian
Multirate implicit Euler schemes for a class of differential{\textendash}algebraic equations of index-1
JCAM :112499
September 2019
Herausgeber: Elsevier {BV}4097.
Bartel, Andreas; Günther, Michael
Multirate Schemes
Novel Mathematics Inspired by Industrial Challenges :5
20194096.
Nanoelectronic Coupled Problems Solutions
In ter Maten, E. J. W. and Brachtendorf, H.-G. and Pulch, R. and Schoenmaker, W. and De Gersem, H., Editor, Band 29 aus Mathematics in Industry
Herausgeber: Springer
20194095.
Tischendorf, Caren; Maten, E. Jan W.; Schoenmaker, Wim
Nanoelectronic coupled problems solutions – Highlights from the nanoCOPS project
In ter Maten, E. Jan W. and Brachtendorf, Hans-Georg and Pulch, Roland and Schoenmaker, Wim and De Gersem, Herbert, Editor aus Mathematics in Industry
Seite 1–21
Herausgeber: Springer Cham
2019
1–214094.
Demirkan, Reşat-Anıl
Neuartige Emulgatoren und deren Eignung für Rapsöl und Rapsölmethylester Emulsionen
20194093.
Schöps, Sebastian; Duque Guerra, David J; De Gersem, Herbert; Bartel, Andreas; Günther, Michael; Pulch, Roland
Non-Intrusive Methods for the Cosimulation of Coupled Problems
Nanoelectronic Coupled Problems Solutions :131--159
2019
Herausgeber: Springer International Publishing
