Multirate
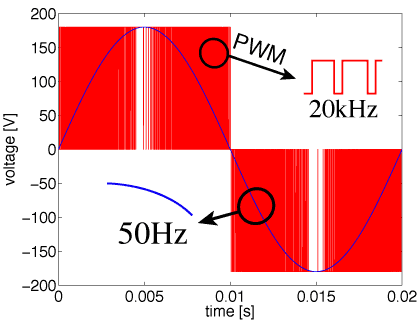
Highly integrated electric cicuits show a phenomenon called latency. That is, a processed signal causes activity only in a small subset of the whole circuit (imagine a central processing unit), whereas the other part of the system behaves almost constant over some time - is latent. Such an electric system can be described as coupled system, where the waveforms show different time scales, also refered to as multirate.
More generally, any coupled problem formulation due to coupled physical effects, may cause a multirate problem: image the simulation of car driving on the road, there you need a model for the wheel, the chassis, the dampers, the road,... (cf. co-simulation). Again each system is covered by their own time constant, which might vary over several orders of magnitude comparing different subsystems.
Classical methods cannot exploit this multirate potential, but resolve everything on the finest scale. This causes an over sampling of the latent components. In constrast, Co-simulation or especially dedicated multirate methods are designed to use the inherent step size to resolve the time-domain behaviour of each subystem with the required accuracy. This requires a time-stepping for each.
Group members working in that field
- Andreas Bartel
- Michael Günther
Former and ongoing Projects
Cooperations
- Herbert de Gersem, K.U. Leuven, Belgium
- Jan ter Maten, TU Eindhoven and NXP, the Netherlands
Publications
- 2025
5412.
[german] Zeller, Diana; Bohrmann-Linde, Claudia; Mack, Nils; Schrader, Claudia
Produktion eigener VR-Lernsettings im Projekt FoPro-VR. Ein interdisziplinärer Lehransatz für die Lehramtsausbildung
In Mrohs, Lorenz; Franz, Julia; Herrmann, Dominik; Lindner, Konstantin; Staake, Thorsten, Editor, Digitales Lehren und Lernen an der Hochschule. Strategien - Bedingungen - Umsetzung
Seite 191-204
Herausgeber: transcript, Bielefeld
2025
191-204ISBN: 9783839471203
5411.
Vinod, Vivin; Zaspel, Peter
QeMFi: A Multifidelity Dataset of Quantum Chemical Properties of Diverse Molecules
Sci. Data, 12 (1) :202
2025
Herausgeber: Nature Publishing Group
ISSN: 2052-44635410.
Xue, Chaoyang; Chen, Hui; McGillen, Max R.; Su, Hang; Cheng, Yafang; Kleffmann, Jörg; Li, Guo; Cazaunau, Mathieu; Colomb, Aurélie; Sciare, Jean; DeWitt, Langley; Marchand, Nicolas; Sarda-Esteve, Roland; Petit, Jean-Eudes; Kukui, Alexandre
Role of Heterogeneous Reactions in the Atmospheric Oxidizing Capacity in Island Environments
Environmental Science & Technology, 59 (6) :3153—3164
Februar 2025
ISSN: 0013-936X, 1520-58515409.
Clément, François; Doerr, Carola; Klamroth, Kathrin; Paquete, Luís
Searching Permutations for Constructing Uniformly Distributed Point Sets
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 122 (14) :e2424464122
20255408.
Heintz, Chris; Kersten, Hendrik; Benter, Thorsten; Wissdorf, Walter
Signatures of Charged Droplets from ESI: A Statistical Analysis of Non-summed Mass Spectra Compared to APCI
Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 36 (4) :839—849
April 2025
ISSN: 1044-0305, 1879-11235407.
Palitta, Davide; Schweitzer, Marcel; Simoncini, Valeria
Sketched and truncated polynomial Krylov methods: Evaluation of matrix functions
Numer. Linear Algebra Appl., 32 :e2596
20255406.
Liu, Qian; Yanchang, Zhang; Zuan, Wang; Wang, Miao; Zhao, Xiaowei
Small-signal stability of sequence-decomposed grid-forming IBRs with DC-link voltage dynamics
Februar 20255405.
Arora, Sahiba; Mui, Jonathan
Smoothing of operator semigroups under relatively bounded perturbations
20255404.
Santos, Daniela Dos; Klamroth, Kathrin; Martins, Pedro; Paquete, Luís
Solving the Multiobejctive Quasi-Clique Problem
European Journal of Operational Research, 323 :409—424
20255403.
Kiesling, Elisabeth
Unterrichtsmaterial Kreislaufwirtschaft - Den Kreislauf in Schwung bringen: Arbeitsblatt: 2.4 Carbon Capture and Stoage und Experiment: 2.5 Modellversuch zur Speicherung von Kohlenstoffdioxid in Kohleflözen
In Dr. Karl Hübner, Prof. Dr. Bernd Ralle, Editor
Herausgeber: Fonds der Chemischen Industrie im Verband der Chemischen Industrie e. V. (FCI)
April 20255402.
[german] Zeller, Diana; Ramella, Abigail; Mack, Nils; Schrader, Claudia; Bohrmann-Linde, Claudia
Virtual Reality im Unterricht – Potentiale und Herausforderungen beim Einsatz von VR im Chemieunterricht
MNU-Journal, 04/2025 :284-289
20255401.
[german] Kiesling, Elisabeth; Bohrmann-Linde, Claudia
Von der Leitlinie BNE zum bilingual-englischen Schülerlabor- Konzeption, Erprobung und Evaluation einer bilingualen Experimentierumgebung im Fach Chemie zum Thema Carbon Capture and Storage
In Andreas Keil, Annika Hanau und Julian Dietze (Hg.): BNE in der Lehrkräftebildung. Erkenntnisse aus Forschung und Praxis., Editor, BNE in der Lehrkräftebildung - Erkenntnisse aus Forschung und Praxis
Seite 327-344
Herausgeber: Waxmann
Mai 2025
327-344ISBN: 978-3-8188-0035-2
5400.
[german] Zeller, Diana; Bohrmann-Linde, Claudia; Mack, Nils; Schrader, Claudia
VR-Lernsettings zum Thema Verbrennungsreaktionen. Ein interdisziplinäres Lehrprojekt zur Produktion von VR-Räumen durch Lehramtsstudierende
In Johannes Huwer, Timm Wilke, Amitabh Banerji, Editor, Band Progress in Digitalisation in Chemistry Education 2024 Digitales Lehren und Lernen an Hochschule und Schule im Fach Chemie
Seite 79-84
Herausgeber: Waxmann Verlag, Münster New York
2025
79-84ISBN: ISBN 978-3-8188-0042-0
5399.
Elghazi, Bouchra; Jacob, Birgit; Zwart, Hans
Well-posedness of a class of infinite-dimensional port-Hamiltonian systems with boundary control and observation
Januar 20255398.
Testa, Filippo
Well-Posedness of the Hodge Wave Equation on a Compact Manifold
20255397.
Acu, A.M.; Heilmann, Margareta; Raşa, I.
Convergence of linking Durrmeyer type modifications of generalized Baskatov operators
Bulleting of the Malaysian Math. Sciences Society5396.
Ehrhardt, Matthias
Ein einfaches Kompartment-Modell zur Beschreibung von Revolutionen am Beispiel des Arabischen Frühlings5395.
Günther, Michael
Einführung in die Finanzmathematik5394.
Al{\i}, G; Bartel, A
Electrical RLC networks and diodes5393.
Gjonaj, Erion; Bahls, Christian Rüdiger; Bandlow, Bastian; Bartel, Andreas; Baumanns, Sascha; Belzen, F; Benderskaya, Galina; Benner, Peter; Beurden, MC; Blaszczyk, Andreas; others
Feldmann, Uwe, 143 Feng, Lihong, 515 De Gersem, Herbert, 341 Gim, Sebasti{\'a}n, 45, 333
MATHEMATICS IN INDUSTRY 14 :5875392.
Ehrhardt, Matthias
für Angewandte Analysis und Stochastik5391.
Ehrhardt, Matthias; Günther, Michael; Striebel, Michael
Geometric Numerical Integration Structure-Preserving Algorithms for Lattice QCD Simulations5390.
High order tensor product interpolation in the Combination Technique
preprint, 14 :255389.
Hendricks, Christian; Ehrhardt, Matthias; Günther, Michael
Hybrid finite difference/pseudospectral methods for stochastic volatility models
19th European Conference on Mathematics for Industry, Seite 3885388.
Ehrhardt, Matthias; Csomós, Petra; Faragó, István; others
Invited Papers
